Introduction
Who does this document target?
This document is intended for the merchants who want to integrate the Mercanet solution in a quick, simple way. It explains how you can start accepting payments with the connector Mercanet Paypage POST without payment pages customisation.
The options described in this guide are the most commonly used.
This guide explains how to accept payments:
- in euros
- with the Visa, Vpay, Electron, Mastercard, Maestro and PayPal means of payment
- secured by 3-D Secure
You use Mercanet Back Office for cash management and receive the reports daily via e-mail.
This document is valid for the version 2.18 and later of the connector.
Prerequisites
Knowledge of standards related to web programming languages used today, such as Java, PHP or .Net, is necessary to develop a connection to Mercanet Paypage POST.
Secret key management
Upon your subscription, BNP Paribas provides a secret key on the Mercanet Téléchargement extranet (please refer to the "Secret key downloading" appendice) that will allow you to secure exchanges between your website and the Mercanet server.
You are responsible for looking after this key and should take all measures to:
- Restrict access to the key
- Safeguard it by encrypting it
- Never copy it onto a non-secure disc or device
- Never send it (via e-mail or regular mail) in a non-secure method.
Mercanet in a nutshell
Mercanet is a secure multi-channel e-commerce payment solution that complies with the PCI DSS standard. It allows you to accept and manage payment transactions by taking into account business rules related to your activity (payment on despatch, deferred payment, recurring payment, payment in instalments, etc.).
You remain free to choose your banking institution and the accepted means of payment.
Mercanet sends activity reports via e-mail on a daily basis:
- the transaction report, which lists all accepted or rejected transactions.
- the operations report, which lists the cash management operations carried out by the merchant.
- the reconciliation report, which provides a financial views of the payments credited to your accounts.
- the chargebacks report, which reconciles the nonpayments of the banking institution (e.g. cardholder challenge) with the transactions that you accepted.
Mercanet provides the Paypage interface for connecting your website to the payment platform.
Paypage works as a direct payment interface with the customer through a Web browser or a mobile device. Therefore, Paypage provides you with ready-to-use secure payment pages that customers can access.
Paypage is complemented by a cash management web interface, Mercanet Back Office, which enables you to create and manage your transactions (validation, cancellation, refund, etc.).
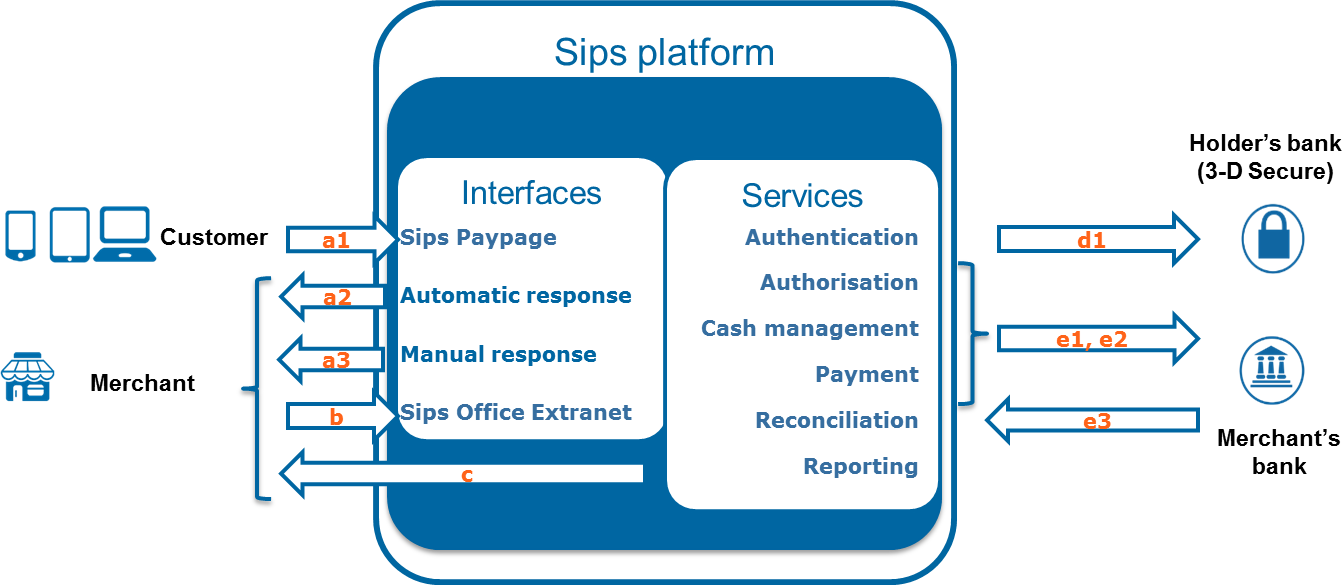
How Paypage works
| Reference | Name | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | Paypage payment request | 24 hours a day | Payment request sent by you to the Mercanet server |
| a2 | Automatic response | 24 hours a day | Response sent by the Mercanet server to you once the payment has been made. This response is sent automatically regardless of what the customer does. |
| a3 | Manual response | 24 hours a day | Response sent by the Mercanet server to you when the customer clicks on “Continue”. The transmission of this response depends on the customer’s action. |
| d1 | Cardholder authentication | 24 hours a day | Request sent to the 3-D Secure authentication server of the cardholder’s bank |
| e1 | Authorisation request | 24 hours a day | Authorisation request sent to your banking institution |
| e2 | Payment remittance | Once a day | Payment remittance from Mercanet to the banking institution in order to credit your account |
| e3 | Payment feedback | 24 hours a day | Banking institution’s feedback on the processing of payment acquiring operations |
| b | Cash management | 24 hours a day | Cash management operation sent by you to the Mercanet server |
| c | Reports | Once a day | Reports sent via e-mail |
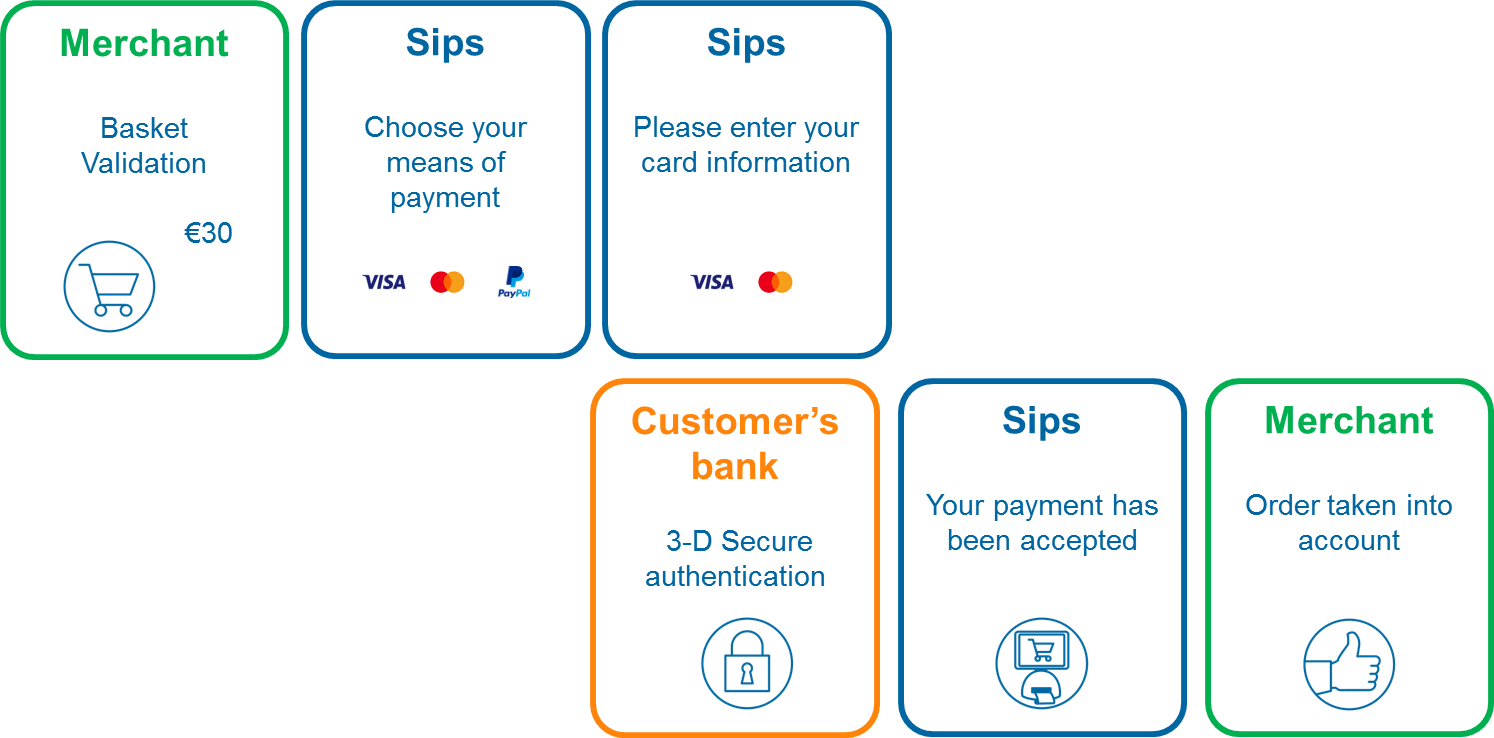
CB, VISA and MASTERCARD transaction process
The customer path consists of the following steps:
- validation of the basket on your merchant page,
- redirection of the customer to the Mercanet page for selecting the mean of payment,
- card data entry,
- customer authentication on a page of their bank (in the case of a 3-D Secure payment),
- display of the sales receipt by Mercanet,
- acknowledgement of the placed order on your merchant page.
In this process the card data entry is handled by Mercanet, and you are not aware of these sensitive data.
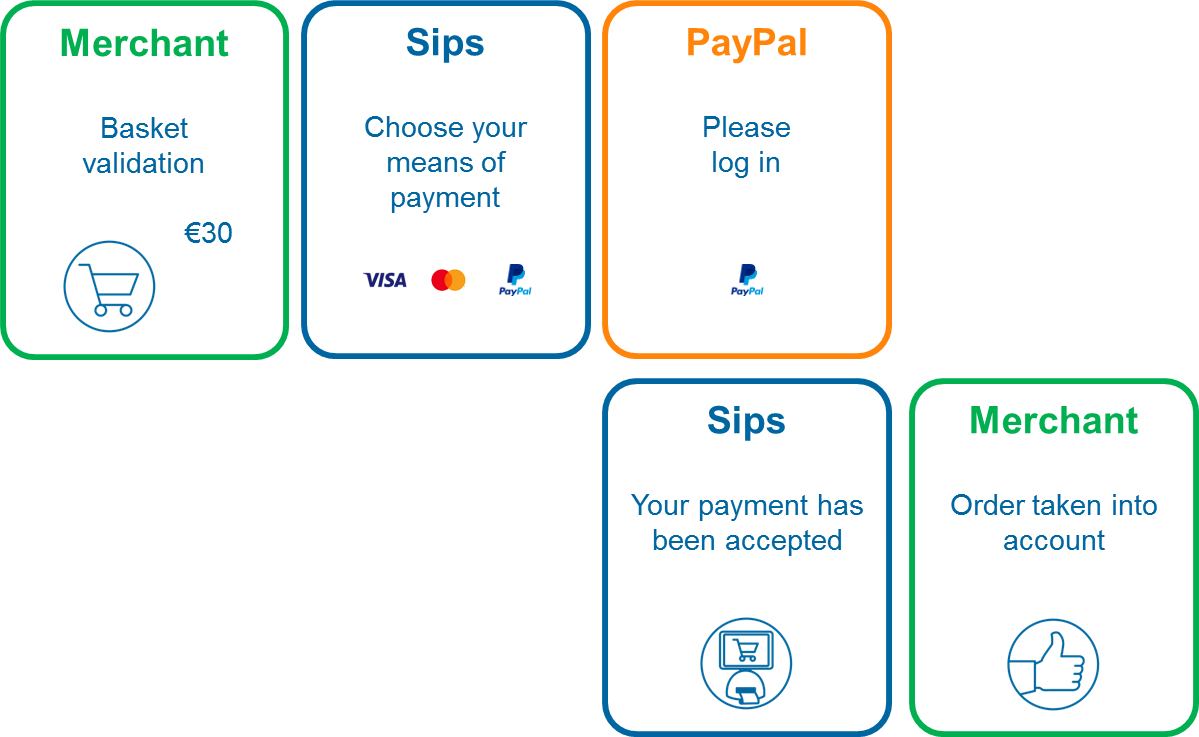
PayPal transactions process
The customer path consists of the following steps:
- validation of the basket on your merchant page,
- redirection of the customer to the Mercanet page for selecting the mean of payment,
- card data entry,
- customer authentication on a PayPal page and means of payment validation,
- display of the sales receipt by Mercanet,
- acknowledgement of the placed order on your merchant page.
Transactions identification
The transactionReference field identifies the transactions of your store in a unique way.
Mercanet (or you) calculates this identifier during the creation of the transaction. The (transactionReference, merchantId) combination identifies the transaction in a unique way throughout the life of the transaction.
5 steps to getting started with Mercanet Paypage POST
To accept payments via Mercanet you must have signed the following documents beforehand:
- a distance selling e-commerce/mail order contract with your bank
- a acceptance contract with the reseller of the Mercanet solution.
Subscription to the 3-D Secure service of Visa and MasterCard, which secures Internet payments, is a mandatory clause of the distance selling contract with your bank.
To be able to accept PayPal payments, you must also have signed a contract with PayPal. Your PayPal merchant account must also be configured to authorise the call to Mercanet (see the “Configuration of the PayPal account” appendix).
Step 1: registering the shop
In order to register your shop as live, you are required to complete the registration form sent by BNP Paribas and send the form back to the latter.
When filling in the form, you must appoint an administrator contact and a technician contact so that BNP Paribas can send you the information needed to launch your shop.
BNP Paribas will then register your shop and e-mail you your merchant ID, together with your IDs and passwords for Merchant Extranet (to retrieve the secret key and perform cash management).
Registering the shop is not needed to start integrating the connector and testing the connection on the customer test environment. It is possible to defer requesting shop registration until you perform live operation tests.
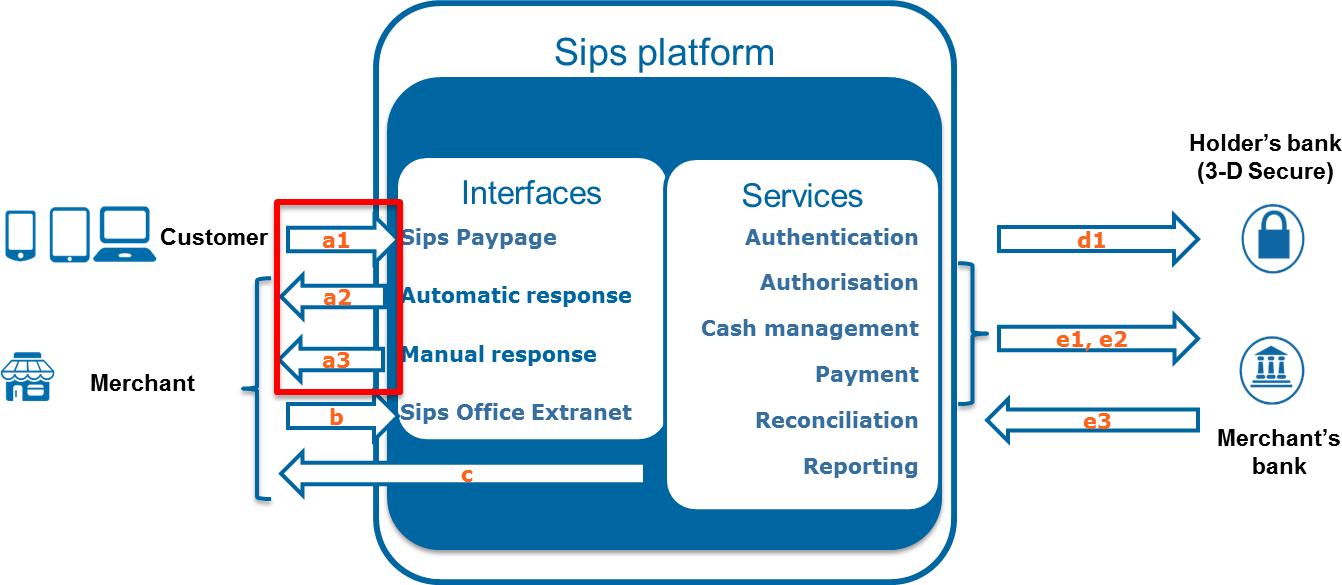
Step 2 - Connecting your site to Paypage
To connect your merchant site to the Mercanet payment server, you must integrate the Mercanet Paypage POST connector.
Therefore, you must set up the links called a1 (payment request), a2 and a3 (payment response) on this diagram:
If the customer does not click on “Return to shop”, the manual response will not be sent, and no Mercanet response will confirm to you that the transaction has been processed.
Generating the payment request
The payment request is sent from a page of your website to the Mercanet server via a Web form with the POST method. This form must point to the URL of the Mercanet payment server and contain the following fields:
| Form data | Presence | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Data | Mandatory | Fields of the payment request (which are described below in the section entitled “Building the payment request: Data field”) |
| InterfaceVersion | Mandatory | The interface version describes the version of the request and the response exchanged with the payment server. The fields described below correspond to the last interfaceVersion. If you use an earlier version of the connector, some fields might be unavailable and therefore unusable. |
| Seal | Mandatory | Signature of the Data field that guarantees the security of the payment request. |
| Encode | Optional | If the Data field contains special characters, you must
change the encoding. The value of the Encode field specifies the
encoding method used for the Data field. If encoding is used, the
seal is calculated for the encoded Data field. Value:
|
| SealAlgorithm | Optional | Algorithm for calculating the hash of the Data
field Value:
|
Building the payment request: Data field
The Data field consists of several fields and contains all the data pertaining to the transaction.
It is supplied as a character string that complies with the following syntax :
<nomChamp1>=<valeurChamp1>|<nomChamp2>=<valeurChamp2>|… |<nomChampN>=<valeurChampN>The Data field must consist of the following fields :
- Mandatory fields
| Fields | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| amount | N12 | Transaction amount. This amount must be sent in the smallest unit of the currency. Example for euros: an amount of 10.50 euros must be sent as 1050. |
| currencyCode | N3 (restricted values / ISO4217) | Transaction currency code. This code is compatible with the ISO-IS 4217 standard. Example: the code for Euro is 978. |
| keyVersion | N10 | Version of the merchant secret key used to compute the seal of the message. E.g. KeyVersion=1 for the first key generated during the registration of the store. |
| merchantId | N15 | Store identifier supplied by Mercanet to the merchant when the latter registers their store. |
| normalReturnUrl | ANS512 (URL) | URL of the merchant used to return to the store if the transaction is accepted. E.g: https://www.monsite.fr/RetourPaiement |
| automaticResponseUrl | ANS512 (URL) | URL supplied by the merchant and used by the payment server
to notify the merchant of the transaction result online and
automatically (automatic response). NB : although this field is not mandatory, it is strongly recommended to implement it so you can receive the payment response even if the customer does not click on “Continue”. |
- Main optional business fields that makes communication easier between your information system and the Mercanet payment server.
| Fields | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| customerId | ANS19 (restrictedString) | Customer ID |
| customerEmail | ANS128 (email) | Customer's e-mail address |
| orderId | ANS32 | Order number associated with the payment transaction. |
| returnContext | ANSU255 (extendedString) | Order context sent in the payment request and reproduced without any change in the response and in the transaction report. You can store in it all the information that will make the response easier to process. |
- CB, Visa, Mastecard, Vpay, Electron and Maestro fields: No specific fields.
- PayPal fields (fields available since version HP_2.18).
| Fields | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| addrOverride | ANS20 (restricted values) | This indicator enables you to:
Value:
|
| invoiceId | AN127 | Order number. It is equivalent to the orderId but must be unique at PayPal. It is mandatory for PayPal to be used. |
| landingPage | AN5 (restricted values) | Indicator that enables you to hide the subscription form on
PayPal pages. Value:
|
| mobile | AN5 (restricted values) | Indicator that enables you to specify if the terminal used
by the customer is the mobile. Value:
|
| orderDescription | ANS127 | Order description |
Securing the request
The request includes the transaction parameters and is sent by the customer's web browser. Theoretically, a third party can intercept the request and modify its content before the data reaches the payment server.
Therefore it is necessary to strengthen security so as to ensure the integrity of the parameters of the transaction sent. The Mercanet solution meets this challenge by exchanging signatures. An effective signature control comprises two elements:
- the integrity of the request and response messages
- the issuer and recipient authentication, as they share the same secret key
Signing the hash of the payment request
The request is secured through the calculation of the hashed value in accordance with the transaction settings (Data field). The secret key is then added to it. All character strings are converted to UTF-8 before the hashing operation.
The hashing algorithm produces an irreversible result that must be sent in hexadecimal form in the POST field named Seal.
When the recipient receives the message, they must recalculate the hashed value and compare it to the value received. Any discrepancy indicates that the exchanged data have been tampered with.
2 methods can be used to sign the hash of the Data field:
For the HMAC-SHA256 algorithm :
- Only the Data field is used (encoded if the relevant option has been selected).
- The secret key is used to generate the HMAC variant of the message.
- The data resulting from previous operation are encoded in UTF-8.
- The bytes obtained are hashed using the HMAC-SHA256 algorithm.
HMAC-SHA256( UTF-8(Data), UTF-8(secreteKey))For the SHA-256 algorithm (although this is the default value, to date, this algorithm is no longer recommended):
- The Data field (encoded if this option has been selected) and the secret key are concatenated.
- The data resulting from the previous operation are encoded in UTF-8.
- The bytes obtained are hashed using the SHA256 algorithm.
SHA256( UTF-8(Data+secretKey))Hmac Sha256 sample code
- Sample Hmac Sha256 encoding in Php 5
<?php … // Seal computation thanks to hash sorted data hash with merchant key $data_to_send= utf8_encode($data) $seal=hash_hmac('sha256', $data_to_send, $secretKey); … … ?>data_to_send and secretKey must use a UTF-8 character set. Please refer to the utf8_encode function for the conversion of ISO-8859-1 characters in UTF-8.
- Sample Hmac Sha256 encoding in Java
import java.security.InvalidKeyException; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; import javax.crypto.Mac; import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec; public class ExampleHMACSHA256 { /** * table to convert a nibble to a hex char. */ static final char[] hexChar = { '0' , '1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' , '6' , '7' , '8' , '9' , 'a' , 'b' , 'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f'}; /** * Fast convert a byte array to a hex string * with possible leading zero. * @param b array of bytes to convert to string * @return hex representation, two chars per byte. */ public static String encodeHexString ( byte[] b ) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer( b.length * 2 ); for ( int i=0; i<b.length; i++ ) { // look up high nibble char sb.append( hexChar [( b[i] & 0xf0 ) >>> 4] ); // look up low nibble char sb.append( hexChar [b[i] & 0x0f] ); } return sb.toString(); } /** * Computes the seal * @param Data the parameters to cipher * @param secretKey the secret key to append to the parameters * @return hex representation of the seal, two chars per byte. */ public static String computeSeal(String data, String secretKey) throws Exception { Mac hmacSHA256 = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256"); SecretKeySpec keySpec = new SecretKeySpec(secretKey.getBytes(), "HmacSHA256"); hmacSHA256.init(keySpec); return encodeHexString(hmacSHA256.doFinal(data.getBytes())); } /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { try { System.out.println (computeSeal("parameters", "key")); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } - Sample Hmac Sha256 encoding in .net
(Carried out using a simple form called "Form1" containing two text fields to enter data and txtSecretKey, and another field to display lblHEX).
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Text; using System.Windows.Forms; using System.Security.Cryptography; namespace ExampleDotNET { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void cmdGO_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { String sChaine = data.Text; UTF8Encoding utf8 = new UTF8Encoding(); Byte[] encodedBytes = utf8.GetBytes(sChaine); byte[] shaResult; HMAC hmac = new HMAC.Create("HMACSHA256"); var key = "YourSecretKey"; hmac.Key = utf8.GetBytes(key); hmac.Initialize(); shaResult = hmac.ComputeHash(encodedBytes); lblHEX.Text = ByteArrayToHEX(shaResult); } private string ByteArrayToHEX(byte[] ba) { StringBuilder hex = new StringBuilder(ba.Length * 2); foreach (byte b in ba) hex.AppendFormat("{0:x2}", b); return hex.ToString(); } } }
Sample Sha256 code
- Sample Sha256 encoding in Php 5
<?php
echo hash('sha256', $data.$secretKey);
?> The UTF-8 character set should be used for the Data and secretKey data. To convert ISO-8859-1 to UTF-8, use the utf8_encode function.
- Sample Sha256 encoding in Java
import java.security.MessageDigest;
public class ExampleSHA256 {
/**
* table to convert a nibble to a hex char.
*/
static final char[] hexChar = {
'0' , '1' , '2' , '3' ,
'4' , '5' , '6' , '7' ,
'8' , '9' , 'a' , 'b' ,
'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f'};
/**
* Fast convert a byte array to a hex string
* with possible leading zero.
* @param b array of bytes to convert to string
* @return hex representation, two chars per byte.
*/
public static String encodeHexString ( byte[] b )
{
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer( b.length * 2 );
for ( int i=0; i<b.length; i++ )
{
// look up high nibble char
sb.append( hexChar [( b[i] & 0xf0 ) >>> 4] );
// look up low nibble char
sb.append( hexChar [b[i] & 0x0f] );
}
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* Computes the seal
* @param Data the parameters to cipher
* @param secretKey the secret key to append to the parameters
* @return hex representation of the seal, two chars per byte.
*/
public static String computeSeal(String Data, String secretKey) throws Exception
{
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
md.update((Data+secretKey).getBytes("UTF-8"));
return encodeHexString(md.digest());
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println (computeSeal("parameters", "key"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}- Sample Sha256 encoding in .NET
Completed using a simple form called "Form 1" containing two text fields to be filled in: data, txtSecretKey and another one to be displayed: lblHEX.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
namespace ExampleDotNET
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void cmdGO_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
String sChaine = data.Text + txtSecretKey.Text;
UTF8Encoding utf8 = new UTF8Encoding();
Byte[] encodedBytes = utf8.GetBytes(sChaine);
byte[] shaResult;
SHA256 shaM = new SHA256Managed();
shaResult = shaM.ComputeHash(encodedBytes);
lblHEX.Text = ByteArrayToHEX(shaResult);
}
private string ByteArrayToHEX(byte[] ba)
{
StringBuilder hex = new StringBuilder(ba.Length * 2);
foreach (byte b in ba)
hex.AppendFormat("{0:x2}", b);
return hex.ToString();
}
}
}Sending the request to Mercanet
The payment request is a HTTPS POST request sent to Mercanet Paypage POST.
Example of a request in the web form (Data field not encoded. The sealAlgotrihm and encode optional fields are not filled in).
<form method="post" action="https://url.vers.serveur.sips/paymentInit">
<input type="hidden" name="Data" value="amount=55|currencyCode=978|merchantId=011223744550001|normalReturnUrl=http://www.normalreturnurl.com|transactionReference=534654|keyVersion=1">
<input type="hidden" name="InterfaceVersion" value="HP_2.18">
<input type="hidden" name="Seal" value="21a57f2fe765e1ae4a8bf15d73fc1bf2a533f547f2343d12a499d9c0592044d4">
<input type="submit" value="Payer">
</form> Error processing
Here is a list of the errors that you might encounter and relevant messages for each. If the error persists, contact the support team.
| Status | Example of an error message | Action to perform |
|---|---|---|
| MerchantId does not exist | Merchant ID (merchantId) not found: findMerchantPoi [220555555550002] is not found [5c62b84e3ae83d] | Compare the merchantId used with the one returned by Mercanet after the registration. |
| Incorrect hashing algorithm | Invalid field value: Invalid sealAlgorithm value (SHA-257) [609eac90a8ee1e]] | Check the seal algorithm used. |
| Secret key error | Invalid signature: rge7gesgd86g556dgv4r89g4d6 [609aec21985569] | The signature that Mercanet calculated upon
receiving the request is not identical to the signature that you
sent.
|
| Invalid key version | Invalid field value : Unable to find a valid key for the following keyVersion=0 [609aec2b60b1d0] | Mercanet does not find the key version that
you have specified (keyVersion field).
|
| Invalid Encode field | Invalid keyword : ENCODE [609aecdee11d52] | Make sure that the encoding algorithm that you use is correctly specified in the encode field. |
| Incorrect return URL | Technical problem : code=30 message=normalReturnUrl is invalid https:// [609aec31b00b94] | Check the syntax of the URL that you specify in the normaReturnUrl field. |
Processing the payment response
When the payment is over:
- Mercanet displays the sales receipt.
- An automatic response is sent to the URL contained in the autoResponseUrl field of the request (this is optional but strongly recommended).
- Mercanet invites the customer to return to your site thanks to the URL specified in the normalReturnUrl field of the request.
Mercanet returns these four fields in responses (automatic and manual):
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Data | Contains the response fields. Complies with the same syntax as the Data field of the payment request. |
| Encode | Type of encoding used. If the value is base64 or base64url, the Data field must be decoded using Base64/Base64Url to find the string of concatenated fields. |
| Seal | Signature of the Data field that guarantees the security of the payment response. |
| InterfaceVersion | Value and version number of the interface used. |
Checking the security of the response
First, you must check the security of the returned message by recalculating the Seal using the same method as the one used for the request. Then, compare the calculated Seal field with the one in the Mercanet response.
If they are identical, process the payment response contained in the Data field.
Otherwise, you must stop processing: check the secret key and the algorithm used, and contact the technical support team if need be.
Analysing the payment response
The payment request contained in the Data field consists of:
- Generic fields
| Fields | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| amount | N12 | Transaction amount. The amount is sent in the smallest unit of the currency. Example for euros: an amount of 10.50 euros must be sent as 1050. |
| currencyCode | N3 (restricted value / ISO4217) | Transaction currency code. This code is compatible with the ISO-IS 4217 standard. |
| customerId | AN19 (restrictedString) | Customer ID |
| customerEmail | ANS128 (email) | Contact's e-mail address |
| transactionReference | AN35 | Transaction identifier unique to each merchant |
| guaranteeIndicator | A1 (restricted values) | Transaction guarantee level (see values in the table below). |
| orderId | ANS32 | Order number associated with the payment transaction. |
| responseCode | N2 (restricted values) | Response code returned by the Mercanet server (see values in the table below). |
| acquirerResponseCode | AN2 (restricted values) | Code returned by the acquirer during an authorisation request (see values in the table below). |
| authorisationId | AN10/ANS32 | Authorisation identifier returned by the authorisation server of the customer bank if the transaction is approved (Not specified if the transaction is refused). |
| maskedPAN | ANS19 | Masked PAN number |
| panExpiryDate | N6 (YYYYMM) | PAN expiry date |
| paymentMeanBrand | ANS20 (restricted values) | Name of the means of payment used by the customer. Values:
|
| returnContext | ANSU255 (extendedString) | Order context sent in the payment request and reproduced without any change in the response and in the transaction report. |
- Fields for card payments
| Fields | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| holderAuthenStatus | ANS20 (restricted values) | Result of the cardholder authentication process (see values in the table below). |
| cardProductCode | AN5 | Card product code |
| cardProductName | ANS70 | Card product wording |
| issuerCode | AN6 | Card issuer code |
| issuerCountryCode | A3 (restricted values) | Card issuer country code |
| issuingCountryCode | A3 (restricted values) | Card issuing country code |
Fields for PayPal payments
No specific fields- Values of the fields to analyse
The responseCode field indicates the acceptance result.
If the value the field responseCode is 00, the payment is accepted.
If the payment is refused (responseCode is different from 00), the acquirerReponseCode field specifies the nature of the bank’s refusal (for a card payment) or the PayPal server’s refusal (for a PayPal payment).
| responseCode | Description | Refusal type |
|---|---|---|
| 00 | Transaction accepted | |
| 05 | Transaction refused | Banking |
| 34 | Suspected fraud (erroneous seal) | Fraud |
| 75 | Maximum number of attempts reached | Means of payment |
| 90 | Service temporarily unavailable | Technical |
| 97 | Session expired (no action from the user during 15 min), transaction refused. | Technical |
| 99 | Temporary problem with the Mercanet server | Technical |
| holderAuthentStatus | Description | 3-D value |
|---|---|---|
| ATTEMPT | The customer did not have to authenticate themselves. | D_ATTEMPT |
| CANCEL | The customer cancelled the authentication process. | 3D_ABORT |
| ERROR | Technical problem during the 3-D Secure authentication | 3D_ERROR |
| FAILURE | The customer could not authenticate themselves (password error). | 3D_FAILURE |
| NOT_ENROLLED | The card used is not enrolled in the 3-D Secure program. | 3D_NOTENROLLED |
| NOT_PARTICIPATING | The customer did not authenticate himself because:
|
SSL |
| SUCCESS | Cardholder authentication successful | 3D_SUCCESS |
| guaranteeIndicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Y | Guaranteed 3-D payment |
| N | Non-guaranteed 3-D payment |
| U | Undefined 3-D guarantee |
| Non-3-D payment |
| acquirerResponseCode | Description | Matching with responseCode |
|---|---|---|
| 00 | Transaction approved or processed successfully | 00 |
| 02 | Contact the issuer of the means of payment | 02 |
| 03 | Invalid receiver | 03 |
| 04 | Keep the medium of the means of payment. | 05 |
| 05 | Do not honour | 05 |
| 07 | Keep the medium of the means of payment, special conditions | 05 |
| 08 | Honour with ID | 05 |
| 12 | Invalid transaction | 12 |
| 13 | Invalid amount | 05 |
| 14 | Invalid means of payment details | 14 |
| 15 | Unknown issuer | 05 |
| 17 | Customer cancellation | 17 |
| 24 | Operation impossible | 05 |
| 25 | Unknown transaction | 05 |
| 30 | Format error | 30 |
| 31 | Id of unknown acquisition organization | 05 |
| 33 | Expired means of payment | 05 |
| 34 | Suspected fraud | 34 |
| 40 | Function not supported | 05 |
| 41 | Lost card | 05 |
| 43 | Stolen card | 34 |
| 51 | Insufficient funds | 05 |
| 54 | Expired card | 05 |
| 56 | No card record | 05 |
| 57 | Transaction not permitted to cardholder | 05 |
| 58 | Transaction not permitted to terminal | 05 |
| 59 | Suspected fraud | 05 |
| 60 | The mean of payment receiver has to contact the acquirer. | 05 |
| 61 | Exceeds withdrawal limit | 05 |
| 62 | Transaction with pending payment confirmation | 05 |
| 63 | Security violation | 05 |
| 65 | Exceeds withdrawal limit | 05 |
| 68 | Response not received or received too late | 05 |
| 75 | Number of attempts to enter the details of the means of payment exceeded | 75 |
| 87 | Unknown terminal | 05 |
| 90 | Momentary shutdown of the system | 90 |
| 91 | Issuer inoperative | 90 |
| 92 | The transaction does not contain sufficient information to be redirected to the duplicate Transaction authorisation agency. | 90 |
| 94 | Duplicate transaction | 90 |
| 96 | System malfunction | 90 |
| 97 | Timeout, transaction refused | 90 |
| 98 | Server unavailable | 90 |
| 99 | Technical incident | 99 |
| A1 | Payment refused by the acquirer (3-D Secure data missing in the authorisation request). | 05 |
Payment response processing
| Status | Response fields | Action to perform |
|---|---|---|
| 3-D Secure payment accepted | responseCode = 00 acquirerResponseCode = 00 guaranteeIndicator = Y,N,U, empty |
You can deliver the order according to the guarantee level of your choice (guaranteeIndicator). |
| 3-D Secure decline | reponseCode = 05 holderAuthenStatus = FAILURE |
Customer authentication failed. This is not necessarily due to fraud. You can suggest your customer to pay with another means of payment and generate a new request. |
| Banking decline | responseCode = 05 | Authorisation refused for a reason not related to fraud. You can suggest your customer to pay with another means of payment and generate a new request. |
| Soft decline | responseCode = 05 acquirerResponseCode = A1 |
The payment has been refused by the acquirer because the
3-D Secure data is missing in the authorisation
request. Please try to pay again with a 3-D Secure payment
process. |
| Fraud-related decline | responseCode = 34 | Authorisation refused because of fraud Do not deliver the order. |
| Decline because of maximum number of attempts reached | responseCode = 75 | The customer has made several attempts, all of which failed
because the information entered was incorrect. There are two
possibilities:
Contact your customer to discuss what should be done
next. |
| Decline because of a technical issue | responseCode = 90, 99 acquirerResponseCode = 90 à 98 |
Temporary technical issue while processing the transaction. Suggest your customer to make another payment later. |
Step 3: testing in the test environment
Once the development of the connection to Mercanet done, you can run a test on the Mercanet server:
Url :
To perform your tests, use the test eshop and the tests cards mentioned on this page :
| merchantId | 211000021310001 |
| scretKey | S9i8qClCnb2CZU3y3Vn0toIOgz3z_aBi79akR30vM9o |
| keyVersion | 1 |
This test eshop only accepts Euro currency.
Step 4 - Validating the connection to the production
Once the connection of your website to has been tested, you can validate the connection to the Mercanet Paypage POST production platform.
To do so, you must change the URL to connect to the Mercanet production server using the credentials received during the registration phase (merchantId, secretKey and keyVersion).
URL Mercanet : https://payment-webinit.mercanet.bnpparibas.net/paymentInit merchantId: Store identifier received via e-mail SecretKey: Secret key that your retrieve from the Mercanet Téléchargement extranet KeyVersion: Secret key version retrieved from Mercanet Téléchargement (logically 1 for the first key) |
We recommend you to isolate your website from the general public beforehand so customers cannot make transactions during this validation phase.
How to validate the proper functioning in the production environment
Immediately:
- Make a transaction using a real payment card (your own, if possible). If the transaction is accepted, it will be sent to the bank to credit your merchant account and to debit the card account.
- Check that your payment pages include your customisation settings.
- Check the transaction via Mercanet Back Office, using the transactionReference.
The next day:
- Make sure the transaction is in the Transactions report.
- Check your account to make sure the operation was credited.
- Refund the transaction via Mercanet Back Office (optional).
Two days later:
- Check that the refund transaction is in the Operations report.
- Make sure the debited amount has been refunded to your merchant account.
This validation process is also applicable to the PayPal means of payment.
Step 5: launching live operation
Once the validation for the transition to live operation has been carried out, make your site and/or application public so your customers can make purchases and payments.
On the same day:
- Monitor acceptance rates (number of responseCode 00 per total number of transactions)
- Check the nature of non-banking declines:
- technical issue: responseCode 90, 99
- fraud: responseCode 34
- maximum number of payment attempts reached: responseCode 75
- abandonment: responseCode 97
The next day:
- Check that all transactions processed (accepted and refused) are in the Transactions report.
- Check the operations you have carried out and remittances (report option) in the Operations report.
Appendices
Creating your PayPal account
You must have a PayPal account in order to use the PayPal mean of payment on your website. It must be a Business account (the type of account is chosen when you register at http://www.paypal.com).
If you have several active shops, we suggest you create a PayPal account for each one.
Setting your PayPal account
On your PayPal account, you as a merchant have to authorise the payment service provider (PSP) to call PayPal API.
In your PayPal Business account, go to Account Settings, then API access:
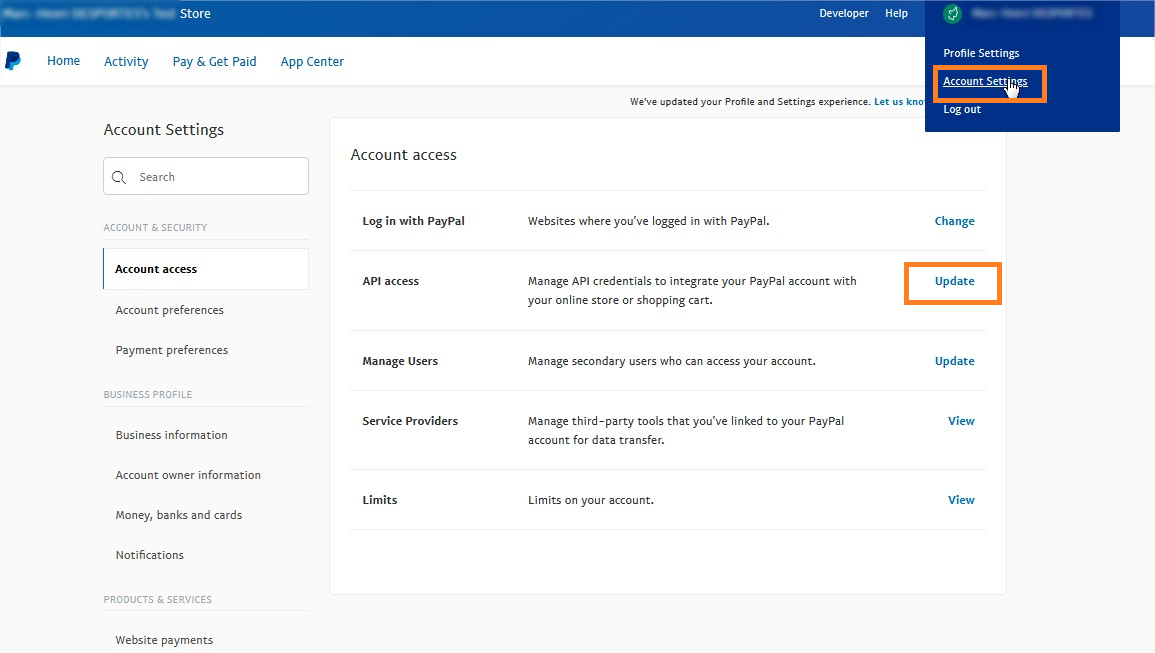
Click on the Pre-built payment solution link.
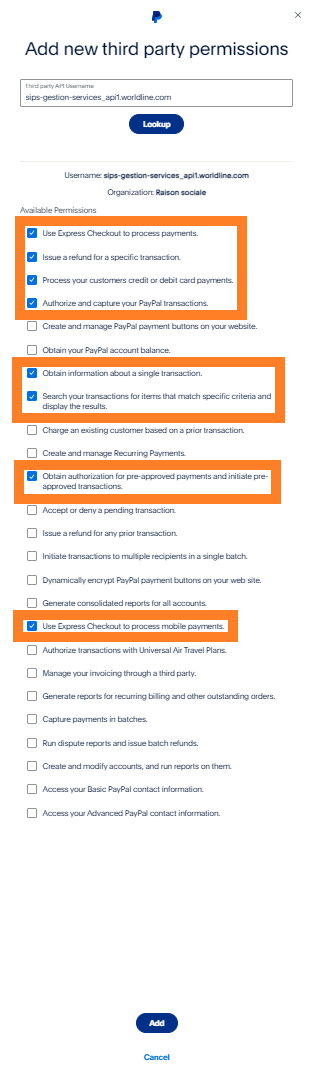
The Add new third-party grant window opens. In the text field, enter the Mercanet technical account sips-gestion-services_api1.worldline.com and click on Search.
Select the following options:
- Use Express Checkout to process payments
- Issue a refund for a specific transaction
- Process your customers credit or debit card payments
- Authorize and capture your PayPal transactions
- Obtain information about a single transaction
- Search your transactions for items that match specific criteria and display the results
- Obtain authorization for pre-approved payments and initiate pre-approved transactions
- Use Express Checkout to process mobile payments
After that, click on the Add button.
If you want to duplicate transactions, you must also select the option "Charge an existing customer based on a prior transaction".
Secret key
Secret key downloading
To access the Mercanet Téléchargement interface, you must first log in to the Merchant Extranet portal via the following URL: https://acces-merchant.mercanet.bnpparibas.net/portal/home with the credentials that were returned to you by Mercanet when your shop was registered:
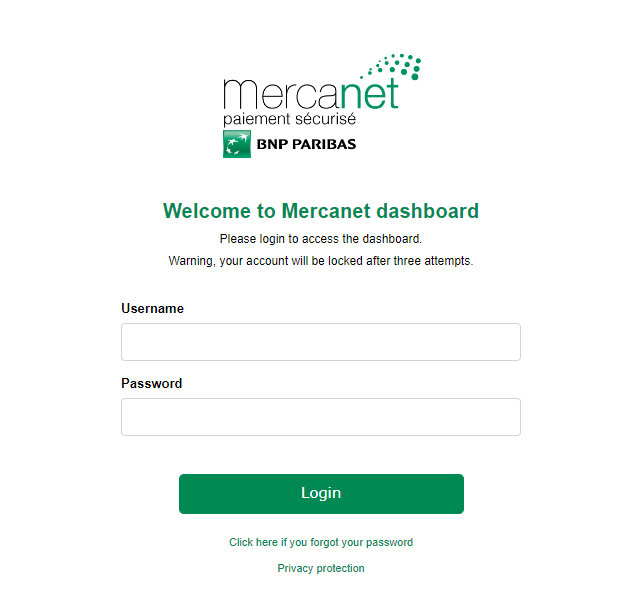
If you have a user with access to multiple webshops, the "Download" tab used for accessing Mercanet Téléchargement is greyed out. To activate it, you have to select a webshop.
Then go to the "Download" tab and "Keys management" tab:
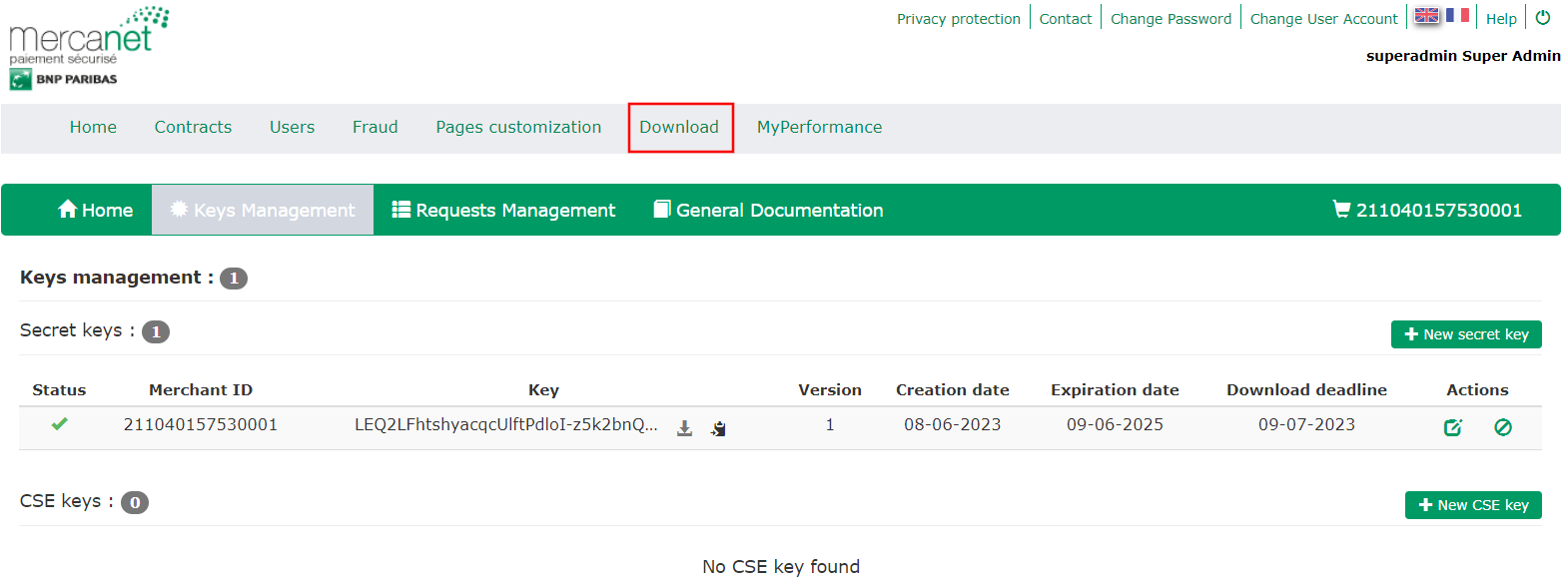
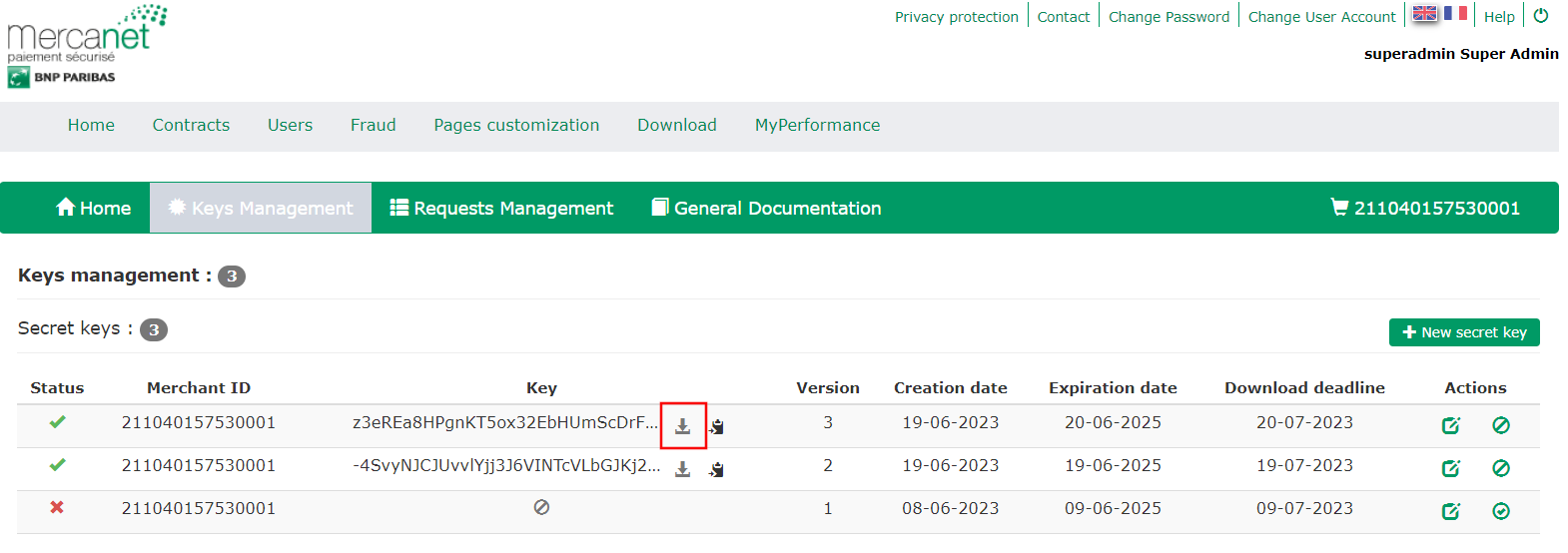
You can now download your secret key:
Payment regulation
The Mercanet solution complies with the regulation in force defined by CB, Visa and Mastercard.
Payment security (PCI)
PCI DSS is an international security standard that aims to guarantee the confidentiality and integrity of cardholders data, thus protecting card and transaction data. You and payment service providers must comply with it at varying degrees according to the importance of their business. The Mercanet solution receives the PCI DSS certification since 2006.
When using Paypage, you do not have access to cardholders data and you do not need to have the PCI DSS certification. Card data are managed by BNP Paribas.
Brand selection during payment (MIF)
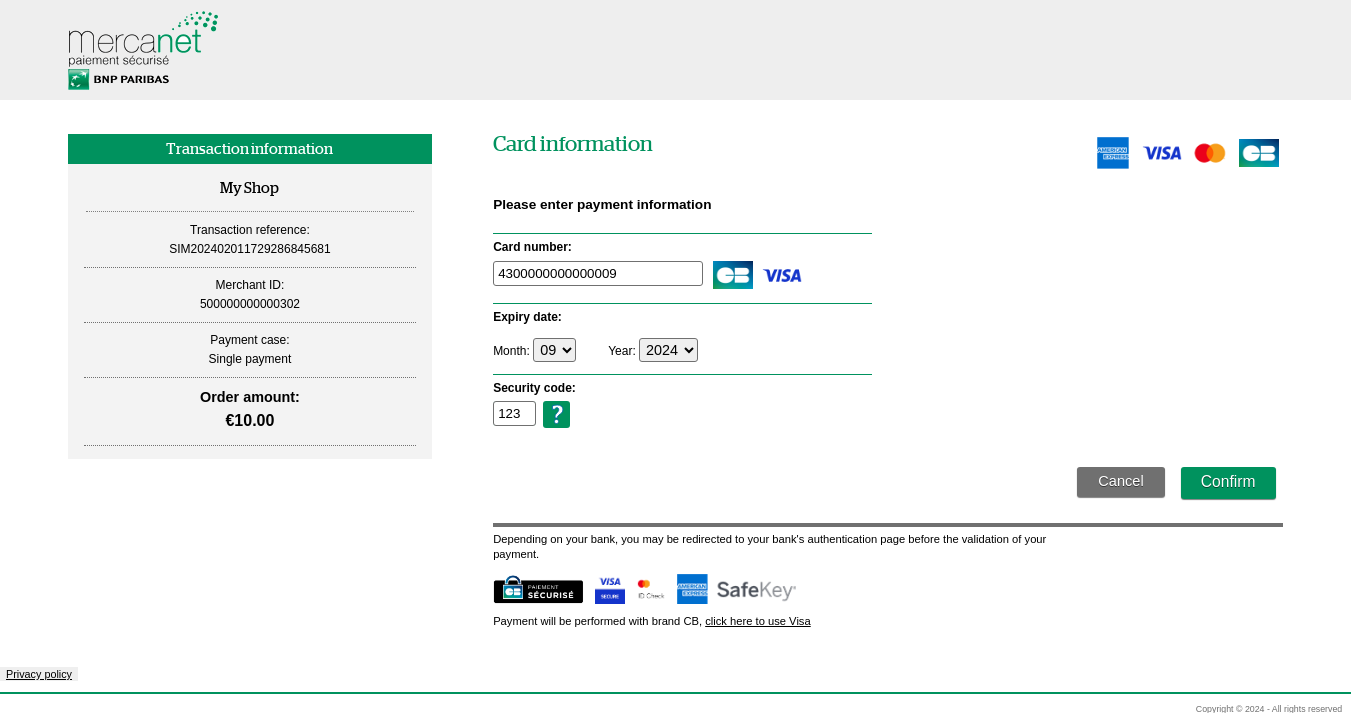
The Mercanet 2.0 solution is subjected to the MIF European regulation (European Official Journal 2015/751 L123 of 19/05/2015). One of its rules, “Brand selection”, requires that you allow holders of co-badged cards to choose the brand that they want to use at the time of payment, which has consequences on the payment page.
A co-branded card supports at least two brands. Most of the cards issued in France are co-badged with CB (CB/VISA, CB/MASTERCARD, CB/MAESTRO, etc.).
You must thus allow the customers who hold such cards to choose the brand to use. The screen below shows an example a CB + Visa co-badged card with CB as the default brand. The customer can change brands by clicking on the link at the bottom of the screen.
For further information
If you want to implement other means of payment or options, please refer to the associated documents.
This non-exhaustive list presents additional documents that will help you implement more Mercanet features.
| Manual | Why read it? |
|---|---|
| Data dictionary | This manual provides the definitions and the values of all the fields of connectors and logs. |
| Functional presentation | This manual provides an overview of Mercanet functionalities and the available options which you can subscribe to. |
| Functionality Set-up guide | This manual explains how to implement Mercanet functionalities. |
| Reports description | This manual describes the content of the logs sent by Mercanet. |
| Paypage customisation for e-shop | This manual explains how to customise payment pages so their graphic charter is the same as that of your site. |
| OneClick | This manual describes the OneClick solution, which enables your customers to pay with one click without having to enter their card data again. |
| Mercanet Message | This manual explains how to implement the Mercanet message solution, which enables you to send e-mail or SMS payment notifications to your customers. |
| Mercanet Téléchargement | This manual explains how to download the documentation and your secret key via the Mercanet Téléchargement extranet. |
| Mercanet Back Office | This manual describes all the cash management operations that can be carried out using Mercanet Back Office. |
| Fraud risk management– GO-no-Go | This manual explains the functioning, configuration and use of the Go-No-Go fraud prevention engine. It enables you to define the fraud-related acceptance rules that you want to implement during payments. |
| Paypage POST | This guide describes and explains how to implement all the options of the connector. |
| American Express integration | This manual explains how to integrate American Express cards. |